Production in a circular economy
Table of Contents
Introduction
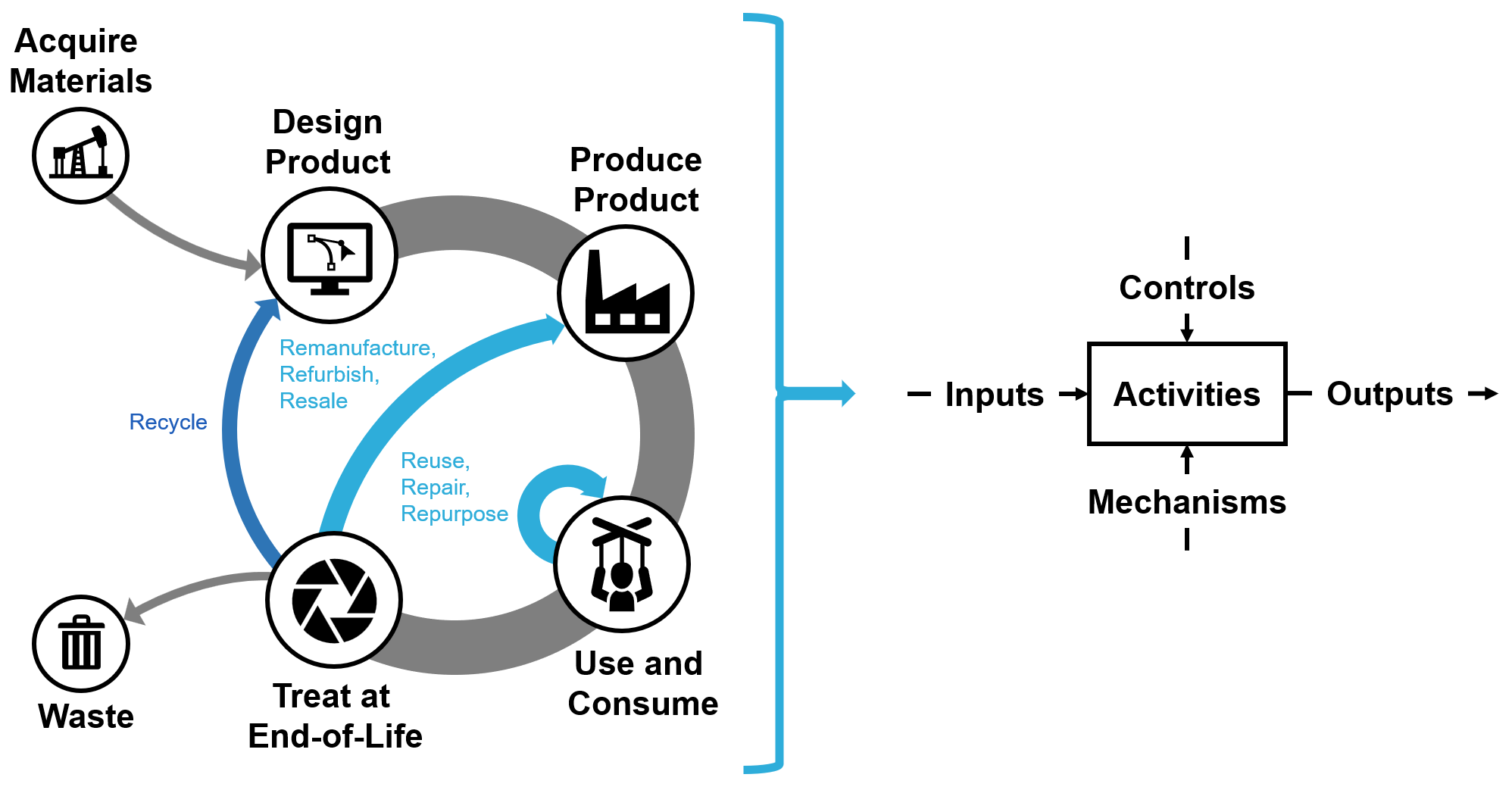
Example pathways that enable the retention of resources, differentiating circular economies from linear economies, as demonstrated in the reference model. Figure adapted from [68].
Purpose: Moving away from a linear economy (take, make, waste) motivates manufacturers to rethink how they design, produce, and ship products. In a circular economy, materials are not discarded after use but brought back into the economy in various ways, spurring industries to find ways to better and more efficiently use resources. A challenge for stakeholders involved in implementing circularity is envisioning and coordinating their individual activities in the context of the entire circular system.
To address this challenge, we introduce a reference model to outline the relevant activities, interactions, and other factors that impact a product life cycle within a circular economy.
Reference Model: The Production in a Circular Economy (CE) Model consists of five life cycle activities (Design Product, Acquire Materials, Produce Product, Use and Consume, and Treat at End of Life) that are consistent with manufacturing economic models. Using the IDEF0 functional modeling method, each activity and its relevant inputs, outputs, controls, and mechanisms are defined. The model is defined for a generic product and may need to be adapted for specific industry sectors. Example use: identifying the organization's reference situation with regards to circular economy and mapping the system to identify where processes can be changed, as indicated by ISO 59004:2024.
To explore the Production in a CE model, select it from the sidebar, or view its decomposition. Visit How to Navigate for details on the model structure. Specific activities that have been explored in depth are described below.
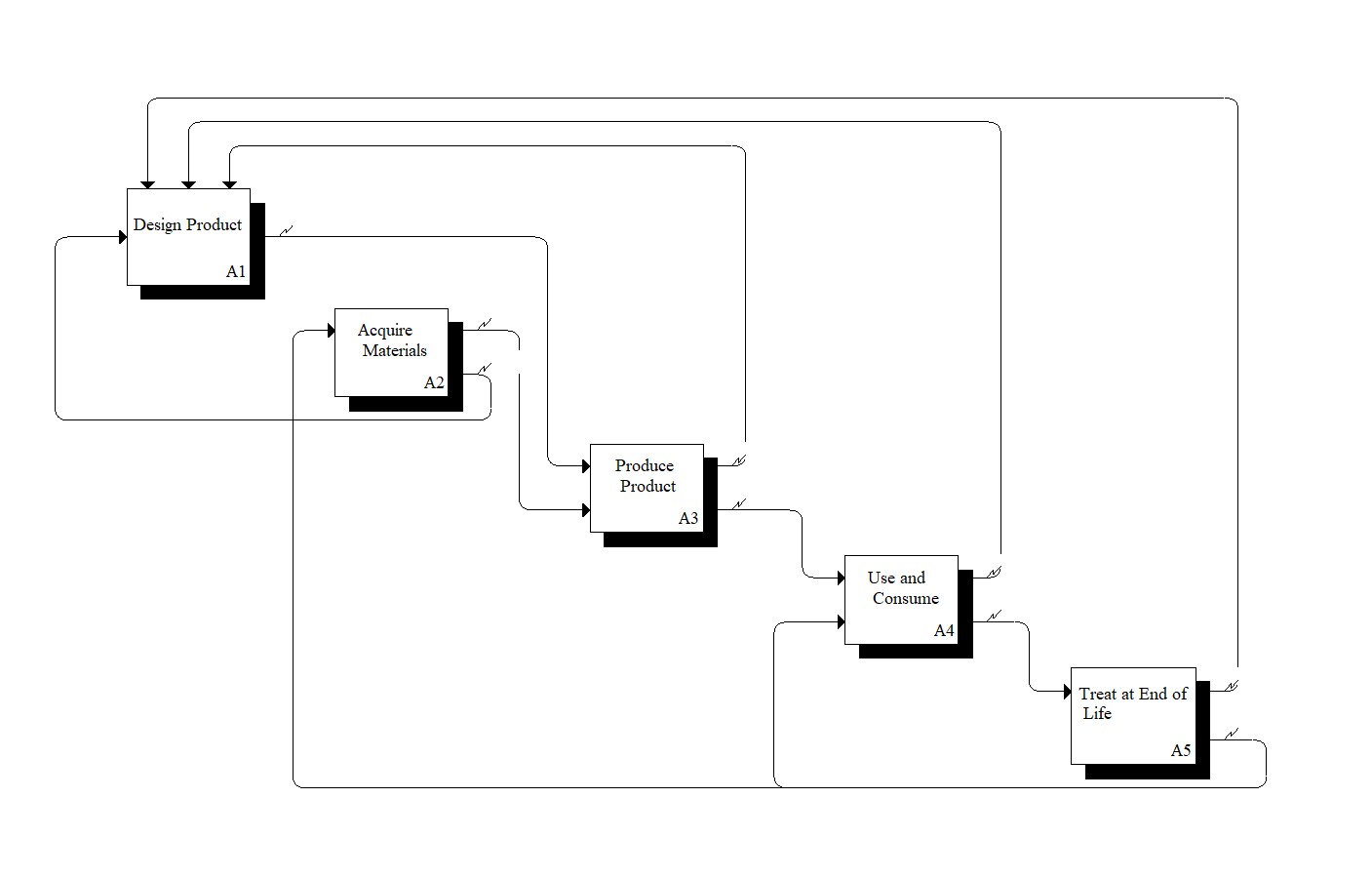
Simplified view of Activities and Inputs, Outputs, Controls, and Mechanisms within the Production in a CE model decomposition. The model provides descriptions and examples of data and materials that may flow across various product life cycle stages.
Citation: https://doi.org/10.18434/mds2-3703
Contact: [email protected]
Model last updated:
Mon May 19 10:06:25 2025
Version: 2
Circular Product Design
The model serves as a resource to:
- Identify differences in data needs and considerations for CPD practices, compared to traditional product design practices
- Identify areas within CPD that require further development of tools, measurement methods, or standards
- Determine the data collection necessary to guide design decisions and assess their downstream impacts
- Plan for information tracking throughout a product life cycle
To explore the design phase only, click the its link or navigate to the activity by expanding the model tree in the sidebar.
Closed Loop Recovery
To explore the end-of-life treatment phase only, click its link or navigate to the activity by expanding the model tree in the sidebar.