Sensors#
Teams are allowed to use sensors to gather information about the environment during competition trials. Sensors can be strategically placed throughout the workspace to inspect cells for defects, monitor conveyor operations, detect object presence, and guide robotic manipulation. The sensor data helps teams make informed decisions about task execution, object handling, and navigation.
Teams are given a budget for their total sensor cost. Each sensor is assigned a grade based on its parameters, and the grade determines its cost. Going over budget will incur a penalty, but staying under will reward bonus points. More information about the associated bonus and penalty can be found on the scoring page.
Common Parameters#
All sensors share the following common configuration parameters:
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique identifier for the sensor |
|
string |
Sensor type (“break_beam”, “distance”, “camera”, or “lidar”) |
|
[float, float, float] |
Position coordinates [x, y, z] |
|
[float, float, float] |
Orientation angles [roll, pitch, yaw] |
|
int |
Frequency of sensor updates (1-30 Hz) |
Break Beam#
The break beam sensor detects when an object interrupts an infrared beam between a transmitter and receiver. It reports binary state information (beam broken/unbroken) and does not provide distance measurements. This sensor is useful for detecting object presence at specific points, such as monitoring conveyor belts. It publishes to these topics.
Break beam sensor#
Break beam sensors use only the common parameters with TYPE set to “break_beam”.
Grade |
Update Rate (Hz) |
Cost ($) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
A |
30 |
400 |
High-frequency detection |
B |
10 |
200 |
Standard detection |
Distance Sensor#
The distance sensor measures the distance to the nearest object in its detection range using ultrasonic or infrared technology. It continuously scans forward and reports distance measurements in meters. This sensor is useful for collision avoidance, proximity detection, and measuring clearances between objects. It publishes to these topics.

Distance sensor#
Distance sensors use only the common parameters with TYPE set to “distance”.
Grade |
Update Rate (Hz) |
Cost ($) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
A |
30 |
600 |
High-frequency ranging |
B |
10 |
300 |
Standard ranging |
RGB Camera#
The RGB camera captures color images of the environment for object detection, identification, and scene analysis. It supports 720p and 1080p resolutions with configurable field of view settings. This sensor can be used for visual recognition, quality inspection, and monitoring tasks. It publishes to these topics.

RGB camera#
RGB cameras use the common parameters with TYPE set to “camera”, plus the following additional parameters:
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
Image resolution (“720p” or “1080p”) |
|
float |
Field of view (0 to \(\pi\) radians) |
Grade |
Update Rate (Hz) |
Resolution |
Cost ($) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A |
30 |
1080p |
800 |
High resolution |
B |
30 |
720p |
500 |
Standard resolution |
Lidar#
The lidar sensor uses laser pulses to create 3D point clouds of the surrounding environment. It performs horizontal and vertical scans with configurable sample rates and angular ranges. This sensor provides precise distance measurements, 3D mapping, and obstacle detection for navigation and spatial analysis. It publishes to these topics.

Lidar#
Lidar sensors use the common parameters with TYPE set to “lidar”, plus the following additional parameters:
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
int |
Number of samples in the horizontal scan |
|
float |
Minimum angle for horizontal scan |
|
float |
Maximum angle for horizontal scan |
|
int |
Number of samples in the vertical scan |
|
float |
Minimum angle for vertical scan |
|
float |
Maximum angle for vertical scan |
Grade |
Update Rate (Hz) |
Sample Limit |
Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
A |
20 |
\(H \cdot V \leq 400\) |
1500 |
B |
10 |
\(200 < H \cdot V \leq 400\) |
1250 |
C |
10 |
\(H \cdot V \leq 200\) |
1000 |
Note
For lidar sensors: \(H\) refers to horizontal samples and \(V\) refers to vertical samples
Bounding Boxes#
Lidar sensors are restricted to physical inspection of battery cells and must be placed within designated bounding boxes around the inspection conveyor. The following table shows the coordinate limits for each available placement area.
Box A |
Box B |
Box C |
|
|---|---|---|---|
X (min, max) |
(0.5, 1.1) |
(0.5, 1.1) |
(0.5, 1.1) |
Y (min, max) |
(0.7, 0.95) |
(1.05, 1.3) |
(0.95, 1.05) |
Z (min, max) |
(0.42, 0.62) |
(0.42, 0.62) |
(0.52, 0.62) |
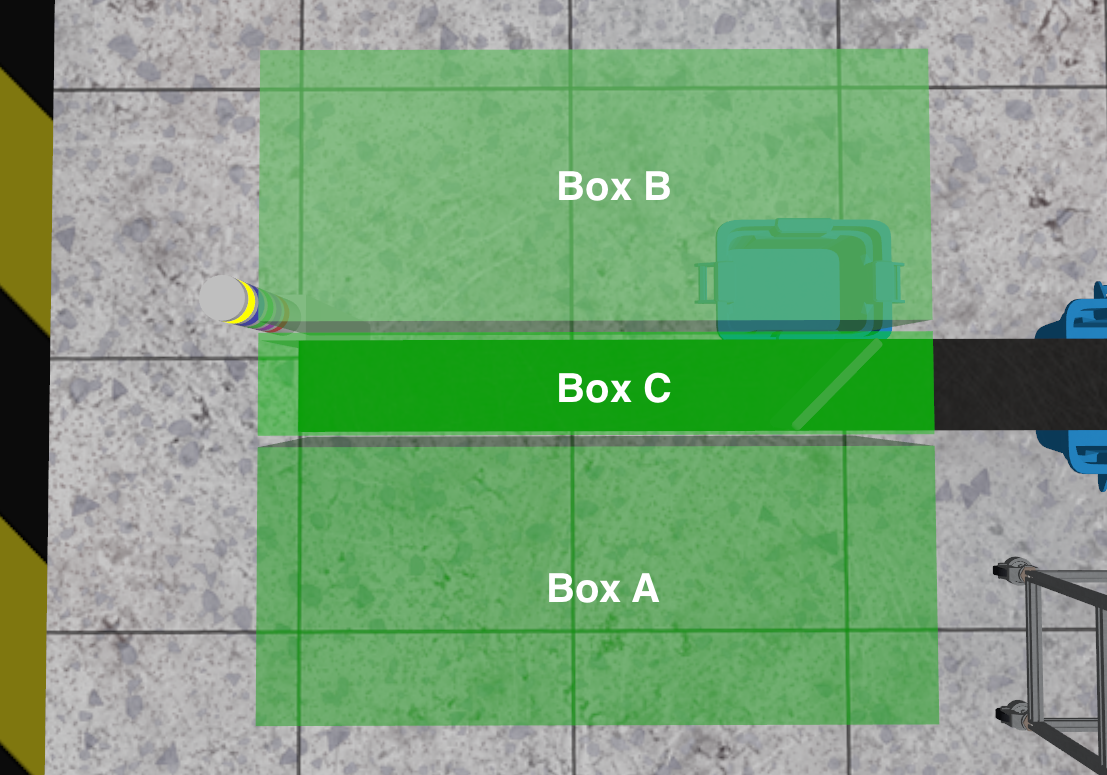
Visualization of the bounding boxes#
Configuration Example#
For complete sensor configuration examples showing all sensor types with valid parameters, see the Sensors Configuration Reference.