6 FpVTE 2012—Class C
Results in this section involve different impression types with all ten fingers. When plain impression fingerprints were used, the configuration contained left slap, right slap, and left and right thumbs (i.e., finger positions 11–14, or a 4-4-1-1 configuration), as both probes and references. Probes were searched against enrollment databases of 5 000 000 subjects containing all ten fingers.
The datasets in this section are equivalent to those used in NIST FpVTE 2012 (Class C). Detailed information about FpVTE 2012 can be found in NIST IR 8034.
Notes:
- No examiner extended feature set data was provided with the images.
- Slap segmentation, if required for the plain impressions, was performed by
tech5impl+0005.
6.1 Template Generation
The approximate total number of records that underwent template generation along with a tally of records that failed to process are shown in Table 6.1. Each template was generated by a single function call providing tech5impl+0005 all of the listed image types.
| Image Contents | Template Type | Failure to Extract | ≈Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Probe | 0 | 30 000 |
| Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0 | 30 000 | |
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Reference | 0 | 5 000 000 |
| Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0 | 5 000 000 |
6.2 Search
The probe templates from Table 6.1 were searched against two enrollment databases of 5 000 000 subjects containing images as specified in the reference template rows of Table 6.1. Approximately one-third of the probes had a corresponding mate in the enrollment database.
6.2.1 DET
The DET plot in Figure 6.1 shows the tradeoff of errors of tech5impl+0005 when searching probe templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C against enrollment databases of 5 000 000 subjects created from the reference templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C where, for approximately one-third of the probes, a single mated identity was present. Tabular versions of FNIR at select FPIR can be viewed in Table 6.2.
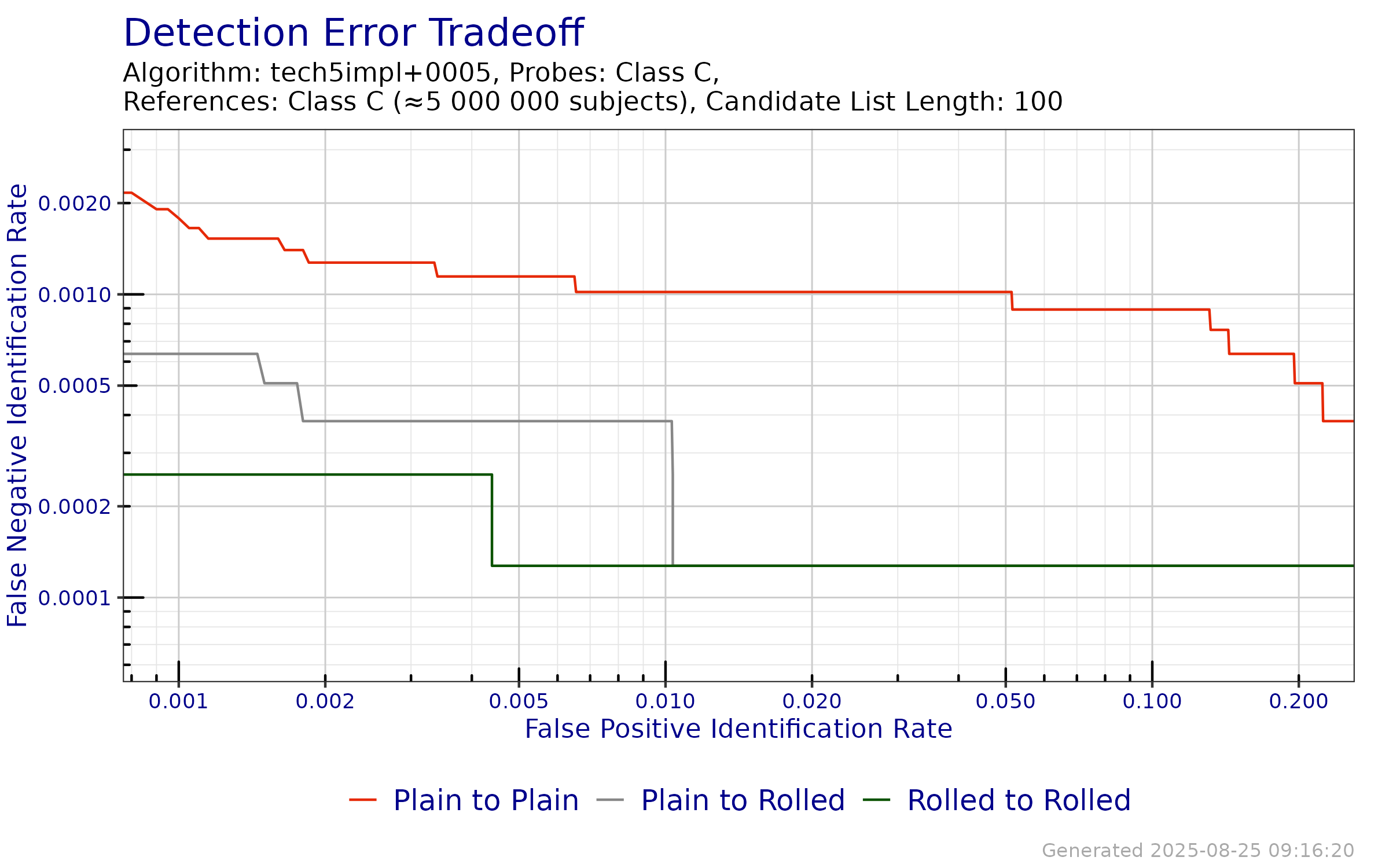
Figure 6.1: DET when searching probe templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C against a enrollment databases generated from reference templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C.
| Probe Content | Reference Content | FPIR ≤ 0.001 | FPIR ≤ 0.005 | FPIR ≤ 0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Plain) | 0.0018 | 0.0011 | 0.0010 |
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.0006 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| Ten Fingers (Roll) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Probe Content | Reference Content | FPIR ≤ 0.001 | FPIR ≤ 0.005 | FPIR ≤ 0.01 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Plain) | 0.2197 | 0.1867 | 0.1770 |
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.1629 | 0.1264 | 0.1202 |
| Ten Fingers (Roll) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.1617 | 0.1343 | 0.1278 |
6.2.2 CMC
The CMC plot in Figure 6.2 show the FNIR of tech5impl+0005 when searching probe templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C against enrollment databases of 5 000 000 subjects created from the reference templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C where, for approximately one-third of the probes, a single mated identity was present. Tabular versions of FNIR at select ranks can be viewed in Table 6.4.
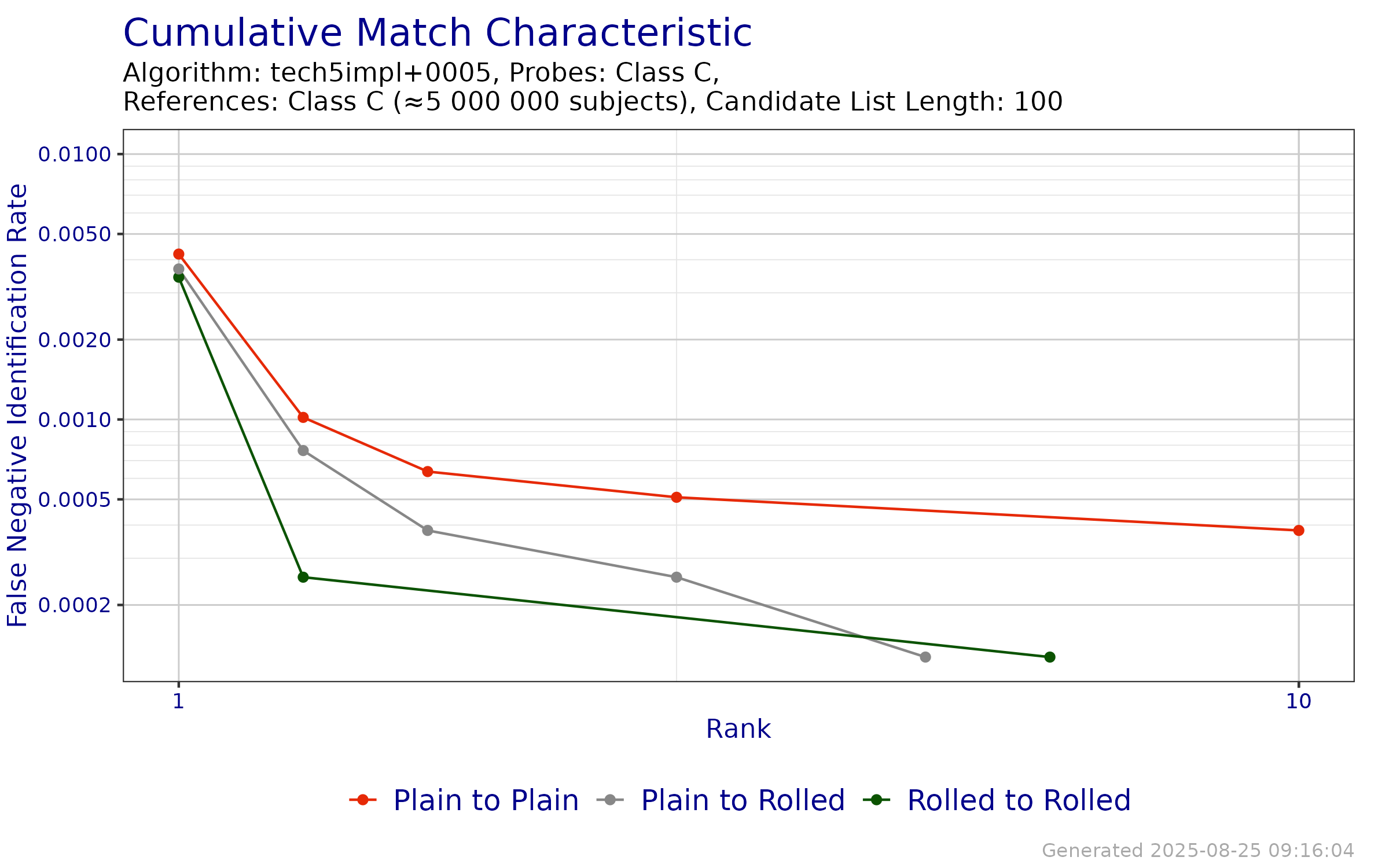
Figure 6.2: CMC when searching probe templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C against enrollment databases generated from reference templates from FpVTE 2012—Class C.
| Probe Content | Reference Content | Rank 1 | Rank ≤ 2 | Rank ≤ 5 | Rank ≤ 10 | Rank ≤ 50 | Rank ≤ 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Plain) | 0.0042 | 0.0010 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| Ten Fingers (Plain) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.0037 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Ten Fingers (Roll) | Ten Fingers (Roll) | 0.0034 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |