class JonesVector
The class JonesVector represents a Jones vector in a Jones representation of polarization states. Arithmetic operations between Jones matrices and Jones vectors, various properties of a Jones vector, and transformation operations are defined.
SCATMECH assumes an exp(-i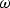 t) time dependence in
the Jones vector. Furthermore, it is assumed that the basis
set for representing the Jones vector, {s,p,k}, is such
that {s,p,k} form a right-handed triplet. With this
convention, (1,i) and (-i,1) represent
left-circularly polarized light, while (1,-i) or
(i,1) represent right-circularly polarized
light.
t) time dependence in
the Jones vector. Furthermore, it is assumed that the basis
set for representing the Jones vector, {s,p,k}, is such
that {s,p,k} form a right-handed triplet. With this
convention, (1,i) and (-i,1) represent
left-circularly polarized light, while (1,-i) or
(i,1) represent right-circularly polarized
light.
Include file:
#include "mueller.h"
Source code:
jvector.cpp
See also:
SCATMECH Home, Conventions, MuellerMatrix, JonesMatrix, StokesVector
C.F. Bohren and D.R. Huffman, Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles, (Wiley, New York, 1983).
H.C. van de Hulst, Light Scattering by Small Particles, (Dover, New York, 1981).
R.A. Chipman, "Polarimetry." in Handbook of Optics, (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995).
Definition of public elements:
class JonesVector {
public:
JonesVector();
JonesVector(const JonesVector& x);
JonesVector(const COMPLEX& s,const COMPLEX& p);
explicit JonesVector(const StokesVector& x);
JonesVector& operator=(const JonesVector& x);
JonesVector operator*(const COMPLEX& x) const;
friend JonesVector operator*(const COMPLEX& x,const JonesVector& y);
JonesVector operator/(const COMPLEX& x) const;
JonesVector& operator*=(const COMPLEX& x);
JonesVector& operator/=(const COMPLEX& x);
JonesVector operator+(const JonesVector& a) const;
JonesVector operator-(const JonesVector& a) const;
JonesVector operator+=(const JonesVector& a);
JonesVector operator-=(const JonesVector& a);
JonesVector operator-() const;
COMPLEX& operator[](int i);
double intensity() const;
double psi() const;
double delta() const;
double eta() const;
double DOLP() const;
double DOP() const;
double DOCP() const;
double e() const;
double epsilon() const;
JonesVector rotate(double angle) const;
COMPLEX& S();
COMPLEX& P();
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,JonesVector& j);
istream& operator>>(istream& is,JonesVector& j);
JonesVector()
Constructor, which does not initialize the vector.
JonesVector(const JonesVector& x)
Copy constructor.
Example:
JonesVector v1; JonesVector v2(v1);
JonesVector(const COMPLEX& a,const COMPLEX& b)
Constructor that assigns values to the elements [S()=a and P()=b].
Example:
JonesVector v(COMPLEX(1,0),0);
explicit JonesVector(const StokesVector& x)
Explicit constructor that converts the polarized part of a StokesVector to a JonesVector. The first element of the JonesVector is left as real, with the relative phase taken up by the second element.
Example:
StokesVector s1; JonesVector j(s1); StokesVector s2(j); // s2 may not be equal to s1
JonesVector& operator=(const JonesVector& x)
Assignment operator.
Example:
JonesVector a,b; a=b;
JonesVector operator*(const COMPLEX& x) const
friend
JonesVector operator*(const COMPLEX& x,const JonesVector& y)
JonesVector operator/(const COMPLEX& x) const
JonesVector& operator*=(const COMPLEX& x)
JonesVector& operator/=(const COMPLEX& x)
Multiplication and division of a JonesVector by a scalar.
Example:
JonesVector vector; COMPLEX scalar; vector = vector*scalar; vector = scalar*vector; // Same thing. vector *= scalar; // Also same thing. vector = vector/scalar; vector /= scalar; // Same thing. vector = scalar/vector; // Not allowed.
JonesVector operator+(const JonesVector& a) const
JonesVector operator-(const JonesVector& a) const
JonesVector operator+=(const JonesVector& a)
JonesVector operator-=(const JonesVector& a)
Addition and subtraction of two JonesVector objects.
Example:
JonesVector vector1,vector2; vector1 = vector1+vector2; vector1 += vector2; // Same thing. vector1 = vector1-vector2; vector1 -= vector2; // Same thing. vector1 = vector2-vector1; // Inverse of previous.
JonesVector operator-() const
Negation of a JonesVector.
Example:
JonesVector vector; vector = -vector;
COMPLEX& operator[](int i)
Element referencing operation.
Example:
JonesVector a; a[0]=1; a[1]=2;
double intensity() const
The intensity associated with the JonesVector.
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "Intensity = " << a.intensity() << endl;
double psi() const
The arctangent of the ratio of the two amplitudes. A value of zero indicates that the p-component of the field is zero.
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "psi = " << a.psi()/PI*180; << " deg" << endl;
double delta() const
The phase between the two components of the JonesVector. A small positive phase indicates that the s-component is in advance of the p-component.
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "delta = " << a.delta()/PI*180; << " deg" << endl;
double eta() const
The principal angle of the polarization. The angle is defined counterclockwise from s, looking into the beam.
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "eta = " << a.eta()/PI*180; << " deg" << endl;
double DOLP() const
double DOP() const
double DOCP() const
The degrees of linear, circular, and total polarization. The degree of circular polarization is positive for left-circularly polarized light.
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "DOLP = " << a.DOLP(); << endl; cout << "DOCP = " << a.DOCP(); << endl; cout << "DOP = " << a.DOP(); << endl;
double e() const
The ellipticity of the field (ratio of minor axis to major axis).
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "ellipticity = " << a.e(); << endl;
double epsilon() const
The eccentricity [sqrt(1-e()^2)].
Example:
JonesVector a; cout << "eccentricity = " << a.epsilon(); << endl;
JonesVector rotate(const double angle) const
Function that returns a JonesVector rotated by an angle. The direction of rotation, for positive angle, is clockwise looking into the beam.
Example:
JonesVector a,b; b=a.rotate(45*PI/180);
COMPLEX& S()
COMPLEX& P()
References to the first (S) and second (P) element of the JonesVector.
Example:
JonesVector a; a.S()=1; a.P()=2;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,JonesVector& j)
Operator that outputs a JonesVector to an output stream. The result contains two complex numbers, separated by a comma, and surrounded by parentheses, e.g., ((1,2),(4,5)). The order of the elements is S and P.
Example
JonesVector J; cout >> "J = " << J << endl;
istream& operator>>(istream& is,JonesVector& j)
Operator that inputs a JonesVector from an input stream. The stream should contain two complex numbers, separated by a comma, and surrounded by parentheses, e.g., ((1,2),(4,5)). The order of the elements is S and P.
Example
JonesVector J; cin << J;
For More Information
SCATMECH Technical Information and Questions
Sensor Science Division Home Page
Sensor Science Division Inquiries
Website Comments
Current SCATMECH version: 7.22 (April 2021)